In many cases, only a fixed set of applications are deployed on an embedded device, making it possible to save resources by minimizing the size of the associated libraries. The Qt installation can easily be optimized by avoiding to compile in the features that are not required.
A wide range of features are defined, covering classes and technologies provided by several of Qt's modules. You can look up the different feature definitions in the
src/corelib/global/qfeatures.txt
file within the Qt source distribution.
To disable a particular feature, just run the
configure
script for Qt for Embedded Linux with the
-no-feature-<feature>
选项。例如:
./configure -no-feature-thread
The feature can easily be enabled again by running
configure
采用
-feature-<feature>
选项。
另请参阅 Qt Performance Tuning .
To disable a particular feature, just run the
configure
script with the set of required
-D<feature>
options. For example, you can use the
-D
option to define
QT_NO_THREAD
:
configure.exe -D QT_NO_THREAD
The
-D
option only creates a Qt internal define. If you get linker errors you have to define
QT_NO_THREAD
also for your project. You can do this by adding
DEFINES
+=
QT_NO_THREAD
to your
.pro
文件。
另请参阅 Qt Performance Tuning .
If you want to disable a lot of features, it is more comfortable to use the
qconfig
tool. You can disable a
set
of features by creating a custom configuration file that defines the preferred subset of Qt's functionality. Such a file uses macros to disable the unwanted features, and can be created manually or by using the
qconfig
tool located in the
tools/qconfig
directory of the Qt source distribution.
注意:
The
qconfig
tool is intended to be built against Qt on desktop platforms.
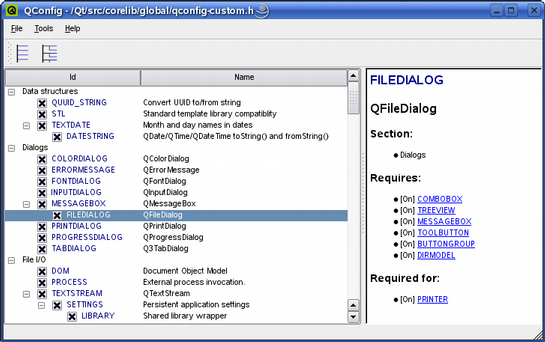
The
qconfig
tool's interface displays all of Qt's functionality, and allows the user to both disable and enable features. The user can open and edit any custom configuration file located in the
src/corelib/global
directory. When creating a custom configuration file manually, a description of the currently available Qt features can be found in the
src/corelib/global/qfeatures.txt
文件。
Note that some features depend on others; disabling any feature will automatically disable all features depending on it. The feature dependencies can be explored using the
qconfig
tool, but they are also described in the
src/corelib/global/qfeatures.h
文件。
To be able to apply the custom configuration, it must be saved in a file called
qconfig-myfile.h
在
src/corelib/global
directory. Then use the
configure
tool's
-qconfig
option and pass the configuration's file name without the
qconfig-
prefix and
.h
extension, as argument. The following examples show how this is invoked on each of the embedded platforms for a file called
qconfig-myfile.h
:
Embedded Linux:
./configure -qconfig myfile
Windows CE:
configure.exe -qconfig myfile
Qt provides several ready-made custom configuration files, defining minimal, small, medium and large installations, respectively. These files are located in the
/src/corelib/global
directory in the Qt source distribution.