Beginning with Qt 4.5, a 部署工具 is included that automates the prodecures described here.
This document describes how to create a bundle and how to make sure that the application will find the resources it needs at run-time. We demonstrate the procedures in terms of deploying the 插件和描绘 application that is provided in Qt's examples directory.
On the Mac, a GUI application must be built and run from a bundle. A bundle is a directory structure that appears as a single entity when viewed in the Finder. A bundle for an application typcially contains the executable and all the resources it needs. See the image below:
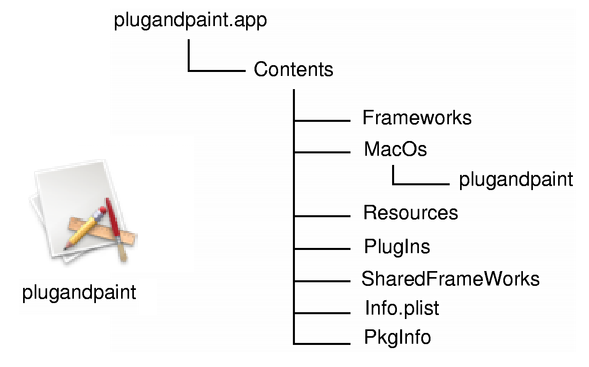
The bundle provides many advantages to the user. One primary advantage is that, since it is a single entity, it allows for drag-and-drop installation. As a programmer you can access bundle information in your own code. This is specific to Mac OS X and beyond the scope of this document. More information about bundles is available on Apple 开发者网站 .
A Qt command line application on Mac OS X works similar to a command line application on Unix and Windows. You probably don't want to run it in a bundle: Add this to your application's .pro:
CONFIG-=app_bundle
This will tell
qmake
not to put the executable inside a bundle. Please refer to the
X11 deployment documentation
for information about how to deploy these "bundle-less" applications.
We will only concern ourselves with command-line tools here. While it is possible to use Xcode for this, Xcode has changed enough between each version that it makes it difficult to document it perfectly for each version. A future version of this document may include more information for using Xcode in the deployment process.
If you want to keep things simple by only having a few files to deploy, then you must build everything statically.
Start by installing a static version of the Qt library. Remember that you will not be able to use plugins and you must build in all the image formats, SQL drivers, etc..
cd /path/to/Qt ./configure -static <other parameters> make sub-src
You can check the various options that are available by running
configure
-help.
Once Qt is built statically, the next step is to regenerate the makefile and rebuild the application. First, we must go into the directory that contains the application:
cd /path/to/Qt/examples/tools/plugandpaint
现在运行
qmake
to create a new makefile for the application, and do a clean build to create the statically linked executable:
make clean
qmake -config release
make
You probably want to link against the release libraries, and you can specify this when invoking
qmake
. If you have Xcode Tools 1.5 or higher installed, you may want to take advantage of "dead code stripping" to reduce the size of your binary even more. You can do this by passing
LIBS+= -dead_strip
to
qmake
in addition to the
-config release
parameter. This doesn't have as large an effect if you are using GCC 4, since Qt will then have function visibility hints built-in, but if you use GCC 3.3, it could make a difference.
Now, provided that everything compiled and linked without any errors, we should have a
plugandpaint.app
bundle that is ready for deployment. One easy way to check that the application really can be run stand-alone is to copy the bundle to a machine that doesn't have Qt or any Qt applications installed, and run the application on that machine.
You can check what other libraries your application links to using the
otool
:
otool -L plugandpaint.app/Contents/MacOs/plugandpaint
Here is what the output looks like for the static 插件和描绘 :
plugandpaint.app/Contents/MacOS/plugandpaint: /System/Library/Frameworks/Carbon.framework/Versions/A/Carbon (compatibility version 2.0.0, current version 128.0.0) /System/Library/Frameworks/QuickTime.framework/Versions/A/QuickTime (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 10.0.0) /usr/lib/libz.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.2.3) /System/Library/Frameworks/ApplicationServices.framework/Versions/A/ApplicationServices (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 22.0.0) /usr/lib/libstdc++.6.dylib (compatibility version 7.0.0, current version 7.3.0) /usr/lib/libgcc_s.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.0.0) /usr/lib/libmx.A.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 92.0.0) /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 88.0.0)
更多信息,见 应用程序依赖 章节。
If you see
Qt
libraries in the output, it probably means that you have both dynamic and static Qt libraries installed on your machine. The linker will always choose dynamic over static. There are two solutions: Either move your Qt dynamic libraries (
.dylibs
) away to another directory while you link the application and then move them back, or edit the
Makefile
and replace link lines for the Qt libraries with the absolute path to the static libraries. For example, replace
-lQtGui
with
/where/static/qt/lib/is/libQtGui.a
The 插件和描绘 example consists of several components: The core application ( 插件和描绘 ), and the 基本工具 and Extra Filters plugins. Since we cannot deploy plugins using the static linking approach, the bundle we have prepared so far is incomplete. The application will run, but the functionality will be disabled due to the missing plugins. To deploy plugin-based applications we should use the framework approach.
We have two challenges when deploying the 插件和描绘 application using frameworks: The Qt runtime has to be correctly redistributed along with the application bundle, and the plugins have to be installed in the correct location so that the application can find them.
When distributing Qt with your application using frameworks, you have two options: You can either distribute Qt as a private framework within your application bundle, or you can distribute Qt as a standard framework (alternatively use the Qt frameworks in the installed binary). These two approaches are essentially the same. The latter option is good if you have many Qt applications and you would prefer to save memory. The former is good if you have Qt built in a special way, or want to make sure the framework is there. It just comes down to where you place the Qt frameworks.
We assume that you already have installed Qt as frameworks, which is the default when installing Qt, in the /path/to/Qt directory. For more information on how to build Qt, see the 安装 文档编制。
When installing, the identification name of the frameworks will also be set. The identification name is what the dynamic linker (
dyld
) uses to find the libraries for your application.
After ensuring that Qt is built as frameworks, we can build the 插件和描绘 application. First, we must go into the directory that contains the application:
cd /path/to/Qt/examples/tools/plugandpaint
Now run qmake to create a new makefile for the application, and do a clean build to create the dynamically linked executable:
make clean
qmake -config release
make
This builds the core application, the following will build the plugins:
cd ../plugandpaintplugins make clean qmake -config release make
现在运行
otool
for the Qt frameworks, for example Qt Gui:
otool -L QtGui.framework/QtGui
You will get the following output:
QtGui.framework/QtGui: /path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui (compatibility version 4.0.0, current version 4.0.1) /System/Library/Frameworks/Carbon.framework/Versions/A/Carbon (compatibility version 2.0.0, current version 128.0.0) /System/Library/Frameworks/QuickTime.framework/Versions/A/QuickTime (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 10.0.0) /path/to/Qt/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore (compatibility version 4.0.0, current version 4.0.1) /usr/lib/libz.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.2.3) /System/Library/Frameworks/ApplicationServices.framework/Versions/A/ApplicationServices (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 22.0.0) /usr/lib/libstdc++.6.dylib (compatibility version 7.0.0, current version 7.3.0) /usr/lib/libgcc_s.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.0.0) /usr/lib/libmx.A.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 92.0.0) /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 88.0.0)
For the Qt frameworks, the first line (i.e.
path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4/QtGui (compatibility version 4.0.0, current version 4.0.1)
) becomes the framework's identification name which is used by the dynamic linker (
dyld
).
But when you are deploying the application, your users may not have the Qt frameworks installed in the specified location. For that reason, you must either provide the frameworks in an agreed upon location, or store the frameworks in the bundle itself. Regardless of which solution you choose, you must make sure that the frameworks return the proper identification name for themselves, and that the application will look for these names. Luckily we can control this with the
install_name_tool
command-line tool.
The
install_name_tool
works in two modes,
-id
and
-change
。
-id
mode is for libraries and frameworks, and allows us to specify a new identification name. We use the
-change
mode to change the paths in the application.
Let's test this out by copying the Qt frameworks into the Plug & Paint bundle. Looking at
otool
's output for the bundle, we can see that we must copy both the
QtCore
and
QtGui
frameworks into the bundle. We will assume that we are in the directory where we built the bundle.
mkdir plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks cp -R /path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks cp -R /path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks
First we create a
框架
directory inside the bundle. This follows the Mac OS X application convention. We then copy the frameworks into the new directory. Since frameworks contain symbolic links, and we want to preserve them, we use the
-R
选项。
install_name_tool -id @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore install_name_tool -id @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui
Then we run
install_name_tool
to set the identification names for the frameworks. The first argument after
-id
is the new name, and the second argument is the framework which identification we wish to change. The text
@executable_path
is a special
dyld
variable telling
dyld
to start looking where the executable is located. The new names specifies that these frameworks will be located "one directory up and over" in the
框架
目录。
install_name_tool -change path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore plugandpaint.app/Contents/MacOs/plugandpaint install_name_tool -change path/to/qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui plugandpaint.app/Contents/MacOs/plugandpaint
Now, the dynamic linker knows where to look for
QtCore
and
QtGui
. Then we must make the application aware of the library locations as well using
install_name_tool
's
-change
mode. This basically comes down to string replacement, to match the identification names that we set for the frameworks.
Finally, since the QtGui framework depends on QtCore , we must remember to change the reference for QtGui :
install_name_tool -change path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore plugandpaint.app/Contents/Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui
After all this we can run
otool
again and see that the application will look in the right locations.
Of course, the thing that makes the 插件和描绘 example interesting are its plugins. The basic steps we need to follow with plugins are:
install_name_tool
While we can put the plugins anywhere we want in the bundle, the best location to put them is under Contents/Plugins. When we built the Plug & Paint plugins, the
DESTDIR
variable in their
.pro
file put the plugins'
.dylib
files in a
plugins
subdirectory in the
plugandpaint
directory. So, in this example, all we need to do is move this directory:
mv plugins plugandpaint.app/Contents
If we run
otool
on for example the
基本工具
plugin's
.dylib
file we get the following information.
libpnp_basictools.dylib: libpnp_basictools.dylib (compatibility version 0.0.0, current version 0.0.0) /path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui (compatibility version 4.0.0, current version 4.0.1) /System/Library/Frameworks/Carbon.framework/Versions/A/Carbon (compatibility version 2.0.0, current version 128.0.0) /System/Library/Frameworks/QuickTime.framework/Versions/A/QuickTime (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 10.0.0) /path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore (compatibility version 4.0.0, current version 4.0.1) /usr/lib/libz.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.2.3) /System/Library/Frameworks/ApplicationServices.framework/Versions/A/ApplicationServices (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 22.0.0) /usr/lib/libstdc++.6.dylib (compatibility version 7.0.0, current version 7.3.0) /usr/lib/libgcc_s.1.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.0.0) /usr/lib/libmx.A.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 92.0.0) /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 88.0.0)
Then we can see that the plugin links to the Qt frameworks it was built against. Since we want the plugins to use the framework in the application bundle we change them the same way as we did for the application. For example for the Basic Tools plugin:
install_name_tool -change /path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore plugandpaint.app/Contents/plugins/libpnp_basictools.dylib install_name_tool -change /path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui plugandpaint.app/Contents/plugins/libpnp_basictools.dylib
We must also modify the code in
tools/plugandpaint/mainwindow.cpp
to
cdUp()
one directory since the plugins live in the bundle. Add the following code to the
mainwindow.cpp
文件:
#elif defined(Q_OS_MAC) if (pluginsDir.dirName() == "MacOS") { pluginsDir.cdUp(); } #endif
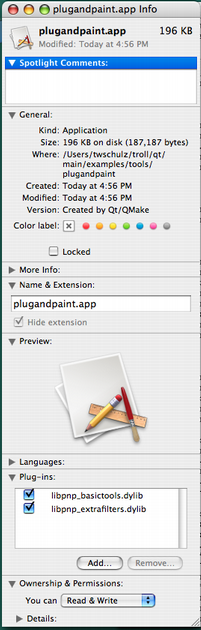
|
The additional code in
tools/plugandpaint/mainwindow.cpp
also enables us to view the plugins in the Finder, as shown to the left.
We can also add plugins extending Qt, for example adding SQL drivers or image formats. We just need to follow the directory structure outlined in plugin documentation, and make sure they are included in the QCoreApplication::libraryPaths (). Let's quickly do this with the image formats, following the approach from above. 把 Qt 的图像格式插件拷贝到捆绑中: cp -R /path/to/Qt/plugins/imageformats pluginandpaint.app/Contents/plugins
使用
install_name_tool -change /path/to/Qt/lib/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtGui.framework/Versions/4.0/QtGui plugandpaint.app/Contents/plugins/imageformats/libqjpeg.dylib install_name_tool -change /path/to/Qt/lib/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore @executable_path/../Frameworks/QtCore.framework/Versions/4.0/QtCore plugandpaint.app/Contents/plugins/imageformats/libqjpeg.dylib
Then we update the source code in
QDir dir(QApplication::applicationDirPath()); dir.cdUp(); dir.cd("plugins"); QApplication::setLibraryPaths(QStringList(dir.absolutePath())); First, we tell the application to only look for plugins in this directory. In our case, this is what we want since we only want to look for the plugins that we distribute with the bundle. If we were part of a bigger Qt installation we could have used QCoreApplication::addLibraryPath () 代替。 |
警告:
When deploying plugins, and thus make changes to the source code, the default identification names are reset when rebuilding the application, and you must repeat the process of making your application link to the Qt frameworks in the bundle using
install_name_tool
.
Now you should be able to move the application to another Mac OS X machine and run it without Qt installed. Alternatively, you can move your frameworks that live outside of the bundle to another directory and see if the application still runs.
If you store the frameworks in another location than in the bundle, the technique of linking your application is similar; you must make sure that the application and the frameworks agree where to be looking for the Qt libraries as well as the plugins.
When you are done linking your application to Qt, either statically or as frameworks, the application is ready to be distributed. Apple provides a fair bit of information about how to do this and instead of repeating it here, we recommend that you consult their software delivery 文档编制。
Although the process of deploying an application do have some pitfalls, once you know the various issues you can easily create packages that all your Mac OS X users will enjoy.
Your application may also depend on one or more Qt plugins, such as the JPEG image format plugin or a SQL driver plugin. Be sure to distribute any Qt plugins that you need with your application, and note that each type of plugin should be located within a specific subdirectory (such as
imageformats
or
sqldrivers
) within your distribution directory, as described below.
注意: If you are deploying an application that uses QtWebKit to display HTML pages from the World Wide Web, you should include all text codec plugins to support as many HTML encodings possible.
The search path for Qt plugins (as well as a few other paths) is hard-coded into the
QtCore
library. By default, the first plugin search path will be hard-coded as
/path/to/Qt/plugins
. But using pre-determined paths has certain disadvantages. For example, they may not exist on the target machine. For that reason you need to examine various alternatives to make sure that the Qt plugins are found:
qt.conf
. This is the recommended approach since it provides the most flexibility.
The 如何创建 Qt 插件 document outlines the issues you need to pay attention to when building and deploying plugins for Qt applications.
You can check which libraries your application is linking against by using the
otool
tool. To use
otool
, all you need to do is to run it like this:
otool -L MyApp.app/Contents/MacOS/MyApp
Unlike the deployment processes on X11 and Windows , compiler specific libraries rarely have to be redistributed along with your application. But since Qt can be configured, built, and installed in several ways on Mac OS X, there are also several ways to deploy applications. Typically your goals help determine how you are going to deploy the application. The last sections describe a couple of things to keep in mind when you are deploying your application.
From Qt 4.6, Mac OS X 10.3 (Panther) is no longer supported. Qt 4.6 applications can be built and deployed on Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger) and higher. This is achieved using weak linking 。在 weak linking , Qt tests whether a function added in a newer version of Mac OS X is available on the computer it is running on. This allows Qt to use newer features, when it runs on a newer version of OS X, while remaining compatible on the older versions.
For more information about cross development issues on Mac OS X, see Apple 开发者网站 .
Since the linker is set to be compatible with all OS X versions, you must change the
MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET
environment variable to get
weak linking
to work for your application. You can add:
QMAKE_MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET = 10.3
to your .pro file, and qmake will take care of this for you.
For more information about C++ runtime environment, see Apple 开发者网站
./CONFIGURE - SDK MacOSX10.4u.sdk
The Qt for Mac OS X libraries, tools, and examples can be built "universal" (i.e. they run natively on both Intel and PowerPC machines). This is accomplished by passing
-universal
在
configure
line of the source package, and requires that you use GCC 4.0.x. On PowerPC hardware you will need to pass the universal SDK as a command line argument to the Qt configure command. For example:
./configure (other arguments) -universal -sdk /Developer/SDKs/MacOSX10.4u.sdk
From 4.1.1 the Qt binary package is already universal.
If you want to create a binary that runs on older versions of PowerPC and x86, it is possible to build Qt for the PowerPC using GCC 3.3, and for x86 one using GCC 4.0, and use Apple's
lipo(1)
tool to stitch them together. This is beyond the scope of this document and is not something we have tried, but Apple documents it on their
developer website
.
Once you have a universal Qt,
qmake
will generate makefiles that will build for its host architecture by default. If you want to build for a specific architecture, you can control this with the
CONFIG
line in your
.pro
file. Use
CONFIG+=ppc
for PowerPC, and
CONFIG+=x86
for x86. If you desire both, simply add both to the
CONFIG
line. PowerPC users also need an SDK. For example:
QMAKE_MAC_SDK=/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX10.4u.sdk CONFIG+=x86 ppc
除了
lipo
, you can also check your binaries with the
file(1)
command line tool or the Finder.
The Mac deployment tool can be found in QTDIR/bin/macdeployqt. It is designed to automate the process of creating a deployable application bundle that contains the Qt libraries as private frameworks.
The mac deployment tool also deploys the Qt plugins, according to the following rules:
注意: If you want a 3rd party library to be included in your application bundle, then you must copy the library into the bundle manually, after the bundle is created.
macdeployqt
supports the following options: